What is 5G RAN
5G RAN is the latest architecture in wireless communication and uses 5G radio frequencies to provide wireless connectivity to devices. A radio access network (RAN) is a key component of a mobile telecommunication system that connects devices like smartphones to a network via a radio link. This is achieved by converting voice and data into digital signals and transmitting them as radio waves to RAN transceivers, which then forward them onto the core network. From the core network, the data can be sent to the internet. RANs perform intense, complex processing.
Why is 5G RAN Important?
Today’s 5G is the result of many years of evolution in RANs. The technology is significantly more complex than 3G and 4G networks as it combines leading-edge technology innovations in 5G new radio air interface and 5G next-generation core network designs. The result is fast, low-latency, high-bandwidth 5G RANs that can connect anything, anywhere, with unparalleled performance, efficiency, and cost. This technology is enabling new innovations in gaming, virtual reality, autonomous driving, mobile edge computing, and a host of other applications.
5G Network Architecture: Requirements and Trends
5G provides greater performance and versatility than previous wireless platforms. That means it requires a more complex and robust infrastructure. Arm and its partners are rapidly resolving every 5G challenge to deliver technology for building seamless networks.
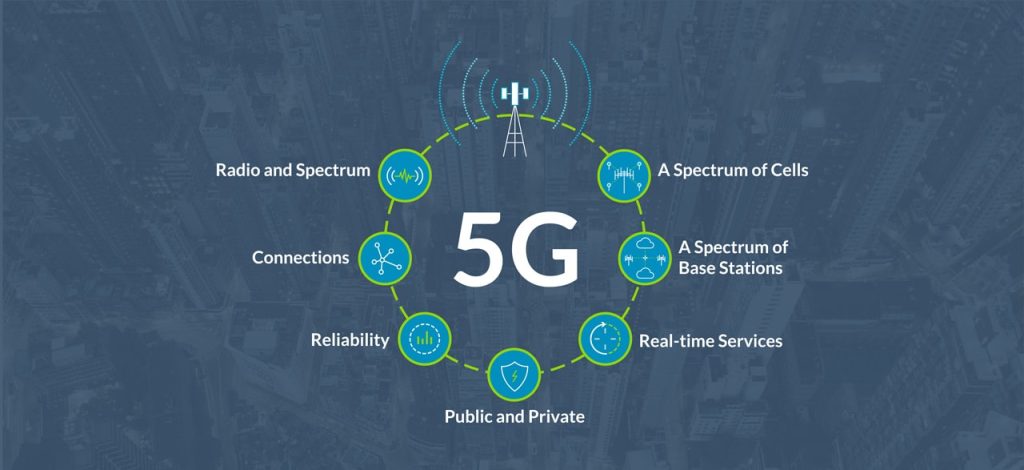
- Radio and Spectrum. 5G features low-band (below 1 GHz), mid-band (1 GHz to 8 GHz), and high-band (24 GHz to 40 GHz) for different applications use cases. Each band has its own set of requirements for performance, capacity, speed, and latency.
- Connections. 5G can support up to a million devices per square kilometer for pervasive IoT services.
- Reliability. Network slicing allows isolated services for greater reliability and quality of service.
- Public and Private. 5G services can be made available through public carriers and be set up to manage discreet facilities, such as factories and other campuses.
- Real-Time Services. Latency can be reduced to up to 1 millisecond to enable effective real-time visibility and control.
- A Spectrum of Base Stations. Outdoor base stations can contain base band units, multiple active antenna units, and edge data servers while pico base stations provide coverage for 40K-50K square feet.
- A Spectrum of Cells. Base stations link to macro cells (10 watts, kilometer ranges), micro cells (5-10 watts, 100s meters), pico cells (100-250 mW, 10s of meters) and femto cells (10-100 mW, meters).
What sets us apart





